
Herceptin‚ Trastuzumab

| What is Herceptin‚? | |
| What are monoclonal antibodies? | |
| Who should take Herceptin‚ ? | |
| Administration | |
| Side Effects | |
| Learn more about breast cancer |

Herceptin‚ is a monoclonal antibody directed against HER-2 (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2) in the treatment of Breast Cancer. HER-2 is overexpressed in 25-30% of breast cancers4 and is a more aggressive form of the cancer. This is a novel drug due to its specific target - the tumor.
This monoclonal antibody was approved by the FDA in September of 1998. The approximate cost is $2100 per vial. The vial can be refrigerated at the location of administration and used for several weekly treatments.

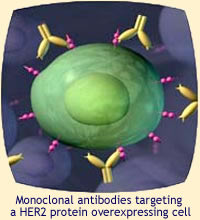
First of all antibodies are part of the body's natural immune defense system. They bind to an antigen (a foreign body) and signal the cell for destruction by natural killer cells. Monoclonal Antibodies are a product of biotechnology. They are directed towards a specific site of action (In Herceptin's‚ case, tumors or HER-2.)

Candidates with breast cancer considering Herceptin‚ therapy must be tested for over-expression of HER-2. There are currently two tests available: DAKO HercepTestô is an IHC (Immunohistochemistry) test and Fluorescence in situ Hybridization (FISH). The tumor tissue is tested, usually after a biopsy or surgery.
Patients with a previous history of cardiac problems or women who are breast feeding are not advised to use Herceptin‚ therapy.

Herceptin‚ is administered in an outpatient setting through an IV infusion. The initial dose is 4 mg/kg followed by a weekly maintenance dose of 2 mg/kg.
Herceptin‚
can also be co-administered with chemotherapy. The New England Journal of
Medicine reports "[C]oncurrent treatment with trastuzumab and first-line
chemotherapy was associated with a significantly longer time to disease
progression, a higher rate of response, a longer duration of response, and
improved overall survival." 2


*Ventricular dysfunction *Congestive Heart Failure *Chills and Fever
*Hypotension *Increased incidence of infections *Dizziness
*Nausea/Vomiting *Pain *Headache

American Cancer Society http://www.cancer.org
Breastcancer.org http://www.breastcancer.org
National Breast Cancer Coalition (NBCC) http://www.natlbcc.org

In February 2001 researchers discovered the exact structure of the HER-2 receptor. This is a big step for Herceptin and other monoclonal antibody therapies. With the knowledge of the structure of HER-2, monoclonal antibodies can be created that have a higher affinity and therapeutic efficacy to the receptor.3


2Slamon D J., Leyland-Jones B, Shak S., Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:783-92.
3HS Cho, K Mason, KX Ramyar, AM Stanley, SB Gabelli, DW Denney Jr, DJ Leahy. Structure of the extracellular region of HER2 alone and in complex with the Herceptin Fab. Nature. Feb. 2001; 756-60.
4 Herceptin Patient-Package Insert. http://www.herceptin.com/herceptin/physician/pi.htm

